What Are the Uses of Drone Surveying?
by siteadmin
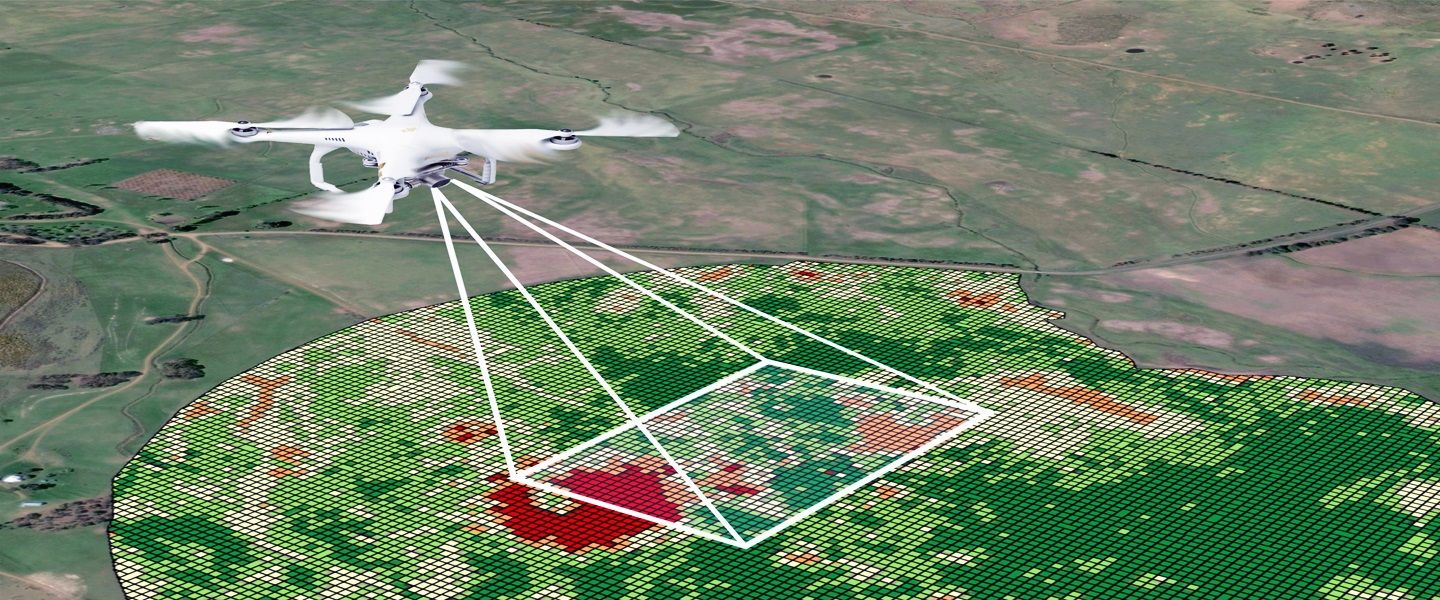
Drone Surveying is a fast and cost-effective way to obtain accurate topographical site data. It also reduces safety liabilities as surveyors don’t have to be on-site or in dangerous locations physically to acquire the data.
A drone flies over an area and captures images which are then processed to create 2D Orthomosaic maps or 3D models. The process of capturing this information is known as photogrammetry.
Land Surveying
A drone land survey is used to establish a property’s boundaries, create legally acceptable subdivisions and evaluate the suitability of a building site before any foundations are put down. This service can also help minimize safety liabilities, since the drone’s operator is operating it remotely and does not have to walk through hazardous areas.
Drones can perform high-quality 3D mapping and distance measurements and can produce an accurate topographic map of a site in just minutes. This data can then be used to generate volumetric measurements of stockpiles, which is useful for companies like mines and quarries who need to calculate their inventories of raw materials. This method of capturing this information is much quicker and more cost-effective than traditional aerial vehicles that would require surveyors to go up and down each stockpile of material.
Additionally, drones can capture data at vantage points that are impossible to access by human operators. This can be helpful for surveys that must be done in harsh or hazardous environments, such as those performed by oil and gas pipeline companies.
For this type of work, the most important thing is to ensure that the drone you choose can operate in these environments. This means ensuring that the drone is equipped with the appropriate sensors for the job and that it can fly safely within the laws of your local municipality or other regulatory bodies.
You can also improve the accuracy of drone mapping by using extra GPS reference points besides visual landmarks, making sure that your equipment is well-maintained and that you work in favorable weather conditions. These improvements will not only increase the accuracy of your drone maps, but they will also help you avoid disputes and misunderstandings over the data.
Another way to improve the accuracy of your drone maps is by stitching together multiple images and analyzing them using a technique called photogrammetry. This will create an orthomosaic, which is a group of images of the same location that have been edited to match each other. This is a common practice for creating base mapping layers and updating them over time on preexisting land-use models.
Construction Surveying
Drone surveys provide a cost-effective and efficient alternative to traditional surveying methods. They can be used to quickly capture data at a wide variety of sites and deliver results to stakeholders in photorealistic 3D maps. This makes it easier to visualize project progress, track work-in-progress, and predict schedule delays or changes. They can also be used to identify survey points and areas that require additional work.
Construction firms use drones to gather accurate and precise topographic data for site planning, design, and construction of roads, buildings, bridges, waterways, and other infrastructure projects. The data helps them reduce costs, save time, and ensure that their work is in compliance with local regulations. In addition, drones can help ensure worker safety by eliminating the need for them to climb dangerous structures or traverse unsafe terrain.
Unlike manned aerial vehicles or satellite imagery, drones can capture topographic data up to five times faster and at a lower cost. They are also not affected by atmospheric conditions, making them a safer alternative to traditional surveying methods. However, to obtain highly accurate drone survey data, a qualified and experienced surveyor must be in control of the aircraft.
The first step in using a drone for a survey is to plan the flight path and determine the type of data you need. Then, you must secure the necessary permissions and clearances from regulatory agencies or property owners. Once you have all the information you need, you can start flying your drone.
Once the drone has collected the data, it is transferred to a computer for processing. Software then stitches the individual images together, creating a cohesive mosaic that represents the entire area. This process is called drone photogrammetry. The data can then be used to create a range of outputs, including orthomosaic maps, digital elevation models (DEM), and 3D models.
The use of drones for land surveying has increased significantly over the past few years, as they have become more affordable and offer more benefits than traditional surveying methods. Drones can fly to vantage points that are inaccessible to humans, and they can take a higher resolution image than traditional cameras. Additionally, they can be equipped with advanced payloads to collect a wider range of data.
Agriculture Surveying
Drones can capture data at vantage points that are difficult or impossible for human surveyors to reach, thus saving time and money. They can also be used in hazardous locations without putting humans at risk. Moreover, unlike traditional methods that take days to collect data, drones can take photos of large areas in just minutes. They can also be used with various payloads such as thermal cameras to help detect issues with irrigation or soil, and to identify pests & diseases.
Agriculture is a major contributor to global warming, and sustainable agricultural practices could be the answer. However, achieving this will require accurate data to inform the process. Using drones for farming surveys will help reduce the time it takes to gather data, and enable a faster response to the changing climate.
Survey drones can fly over large areas of land and capture imagery that is tagged with geographical information (X, Y, Z). This enables the drone to produce high-resolution orthomosaic maps or 3D models. It will then be able to extract data that can be used by farmers to plan their crops and ensure optimal harvesting.
In addition, survey drones can be equipped with LiDAR sensors to generate high-resolution point clouds that can be used for 3D modeling and mapping. This data can be used to model the surface of a property or even to create an underground map. This technology is useful for engineering, archaeology, and environmental studies.
Drone mapping is extremely helpful for farmers as it enables them to monitor the condition of their crops. This allows them to identify issues such as nitrogen depletion and fertilizer burn, and respond accordingly. This helps in increasing yields and reducing the costs of production.
Lastly, by using aerial imaging to measure the crop distribution, it becomes easier for farmers to plan their planting and irrigation ahead of time. This leads to more efficient and effective farming, which is a win-win situation for everyone involved.
Drone surveying can be done from a remote location, which will make it safer for workers at the construction site. This will also enable them to keep a close eye on the progress of the project and ensure that it is being carried out according to the design.
Environmental Surveying
Whether they are performing an environmental site assessment or tracking progress on a worksite, drones can help surveyors get the job done faster and more accurately than ever before. Using a surveying drone for your project can reduce the need for manual labor and equipment on site, resulting in significant cost savings.
Drones are also safer than traditional surveying methods, as they don’t require surveyors to walk into dangerous or difficult-to-reach areas on a construction site. This helps minimize safety liabilities and ensures that everyone is as safe as possible while completing the survey.
A drone’s onboard camera captures a series of aerial photos of the survey area, which are then processed and stitched together using photogrammetry software. The resulting data can be used to create a variety of outputs, including orthomosaic maps, digital elevation models (DEM), 3D models, contour lines and vegetation health maps.
When it comes to urban planning, drones are ideal for capturing up-to-date data of cityscapes and landforms. These images can then be analyzed and used to improve the environment, safety and aesthetics of an urban area.
In addition to using RGB and multispectral cameras, many drones can be fitted with LiDAR payloads that can collect a range of information. When combined with other sensors, this allows for more sophisticated outputs such as 3D point clouds, volumetric measurements and surface models.
Once the data has been captured, it’s usually imported into a processing platform such as Propeller for further analysis. This can be done automatically, or manually based on time-stamped coordinates. Propeller also uses post-processing kinematic (PPK) technology to correct any inaccurate onboard GPS data, ensuring accurate geo-tagging of the imagery.
Drones are incredibly versatile and can be used in a variety of different ways for surveying, mapping and topographic work. Before you invest in a drone for your business, make sure to choose one that is best suited to the type of surveying you need and check with local law enforcement to see if there are any restrictions on where you can fly. Once you have the right drone, be sure to use it regularly and update your data often. This will help your team stay on track to meet project deadlines and ensure that any potential issues are resolved as early as possible.
Drone Surveying is a fast and cost-effective way to obtain accurate topographical site data. It also reduces safety liabilities as surveyors don’t have to be on-site or in dangerous locations physically to acquire the data. A drone flies over an area and captures images which are then processed to create 2D Orthomosaic maps or 3D…
Recent Posts
- Affordable Fencing Solutions: Fence Company Rochester NY Offers Insight on the Cheapest Fence Installations in Rochester, NY
- Affordable Fencing Solutions: Fence Company Rochester NY Offers Insight on the Cheapest Fence Installations in Rochester, NY
- Exploring the Drawbacks of Duct Cleaning: Insights from Air Vent Cleaning Charlotte
- Exploring the Drawbacks of Duct Cleaning: Insights from Air Vent Cleaning Charlotte
- Clearing the Dust: Duct Cleaning Louisville KY Shares Tips to Make Your Home Less Dusty
